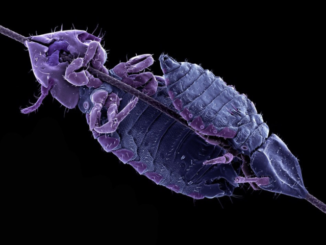
On the relationship between body condition and parasite infection in wildlife: a review and meta‐analysis
Corresponding Author: Daniel Becker, daniel.becker3@montana.edu Summary Author: Leah Crone, lec62627@uga.edu Parasites are thought to be detrimental to their host by burdening host resources, damaging host tissue, and altering host behavior. Thus, ecologists might expect a negative relationship between parasite infection and host condition. However, many studies challenge this expectation and […]